6. Automated and Emerging Technologies
SECTION 1: THEORY FUNDAMENTALS
Important Note
These notes cover the main points for revision. They are great for reviewing key concepts, but for in-depth understanding, always keep your textbook nearby for reference.
Automated and emerging technologies represent the cutting edge of computer science, combining hardware, software, and intelligent systems to create solutions that can operate with minimal human intervention. This chapter explores automated systems, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
Table of Contents
6.1 Automated Systems
6.2 Robotics
6.3 Artificial Intelligence
6.1 Automated Systems
An automated system is a system that can operate with minimal or no human intervention. It uses sensors to collect data, microprocessors to process information, and actuators to perform actions based on the processed data.
6.1.1 Components of Automated Systems
Sensors
Devices that detect and measure physical properties from the environment and convert them into electrical signals.
- • Input devices
- • Convert physical data to digital
- • Examples: Temperature, Light, Pressure
Microprocessors
Process the data received from sensors and make decisions based on programmed instructions.
- • Process sensor data
- • Execute control logic
- • Send signals to actuators
Actuators
Output devices that convert electrical signals into physical actions or movements.
- • Output devices
- • Perform physical actions
- • Examples: Motors, Valves, Pumps
6.1.2 How Automated Systems Work
Sensor Detection
Sensors detect changes in the environment (e.g., temperature drops, motion detected)
Data Processing
Microprocessor receives sensor data, processes it, and compares it with predefined presets
Decision Making
Based on programmed logic, the system decides what action to take
Action Execution
Actuators perform the required action (e.g., turn on lights, open valve, start motor)
6.1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- ✓24/7 Operation: Can work continuously without breaks
- ✓Consistency: Performs tasks with high precision and repeatability
- ✓Cost Reduction: Reduces labor costs and human error
- ✓Safety: Can operate in hazardous environments
- ✓Efficiency: Faster response times than human operators
- ✓Data Collection: Continuously monitors and records data
Disadvantages
- ✗Initial Cost: High setup and installation costs
- ✗Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance and updates
- ✗Unemployment: Can replace human workers
- ✗Lack of Flexibility: Cannot adapt to unexpected situations not programmed
- ✗Dependency: System failure can cause complete shutdown
- ✗Security: Vulnerable to cyber attacks if connected to networks
6.1.4 Examples of Automated Systems
MarkScheme Template
General Process Structure:
- •Sensor continuously monitors the environment
- •ADC (Analogue-to-Digital Converter) converts sensor data from analogue to digital
- •Data is compared to stored values (preset/range)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE:
- - Actuator is activated until values return to the range
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE:
- - No Action taken
- •Whole process repeats continuously
Example Question
Past PaperJamelia has a greenhouse that she uses to grow fruit and vegetables. She needs to make sure the temperature in the greenhouse stays between 25°C and 30°C (inclusive). A system that has a temperature sensor and a microprocessor is used to maintain the temperature in the greenhouse. The system will:
- • open a window and turn a heater off if it gets too hot
- • close a window and turn a heater on if it gets too cold.
Describe how the system uses the temperature sensor and the microprocessor to maintain the temperature in the greenhouse.
Mark Scheme Answer (Eight points from):
- •Sensor sends data/readings/signal to microprocessor
- •Data is converted from analogue to digital (using ADC)
- •Microprocessor compares/checks data to stored values/range of values
- •If data is greater than 30 / above the range, microprocessor sends signal to open window and to turn heater off
- •If data is below 25, the microprocessor sends signal to turn on heater and to close window
- •If data is between 25 and 30 / within the range, no action taken
- •Actuator is used to operate heater/window
- •Whole process is continuous
Automatic Street Lighting
How it works:
- •Light sensor continuously monitors ambient light levels
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares light level with stored preset value
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (below preset/dusk):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (relay/switch)
- - Actuator turns on street lights until light level returns to range
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (above preset/daylight):
- - No Action - lights remain off
- •Whole process repeats continuously
Automatic Water Tank System
How it works:
- •Water level sensor continuously monitors tank water level
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares water level with stored values (minimum and maximum presets)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (below minimum preset):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (water pump)
- - Actuator turns on pump until water level returns to range
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (above maximum preset):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to deactivate actuator to prevent overflow
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (between minimum and maximum):
- - No Action - pump remains off
- •Whole process repeats continuously
Automatic Doors
How it works:
- •Motion/proximity sensor continuously monitors for approaching persons
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares sensor data with stored values (presence detected or not)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (person detected):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (motor/linear actuator)
- - Actuator opens door until person passes
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (no person detected):
- - After set time, actuator closes door
- - Safety sensors prevent closing if someone is in the way
- •Whole process repeats continuously
Central Heating System
How it works:
- •Temperature sensor continuously monitors room temperature
- •User sets desired temperature (stored as preset value)
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares temperature with stored preset value
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (below set point):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (boiler/heater control valve)
- - Actuator turns on heating until temperature returns to range
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (at desired temperature):
- - No Action - heating remains off
- •Whole process repeats continuously
Security Alarm System
How it works:
- •System is armed when user leaves (via keypad or remote)
- •Motion sensors and door/window sensors continuously monitor the area
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares sensor data with stored values (movement detected or not)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (movement or door/window opening detected):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (siren, alarm lights)
- - Actuator activates alarm until system is disarmed
- - System may also send alert to security company or owner's phone
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (no movement detected):
- - No Action - system continues monitoring
- •Whole process repeats continuously while system is armed
Automatic Washing Machine
How it works:
- •User selects wash program and loads clothes
- •Weight sensor continuously monitors amount of laundry
- •Water level sensor continuously monitors water level during filling
- •Temperature sensor continuously monitors water temperature
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares sensor data with stored values (required water level, temperature, etc.)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (water level below required, temperature below set point):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (water valve, heater, motor)
- - Actuator operates until values return to range
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (correct water level and temperature):
- - No Action - proceeds to next cycle
- •Whole process repeats continuously through all cycles until complete
Traffic Light System
How it works:
- •System operates on a timer-based cycle or uses vehicle sensors continuously (induction loops) to detect traffic
- •Sensor data is converted from analogue to digital using ADC
- •Sensor sends signal/data to microprocessor
- •Microprocessor compares sensor data with stored values (presence of vehicles, timing presets)
- •IF OUTSIDE THE RANGE (vehicles detected, timer expired):
- - Microprocessor sends signal to actuator (traffic light relays/switches)
- - Actuator changes lights (red → amber → green) based on traffic flow
- •IF WITHIN THE RANGE (no vehicles, within timing cycle):
- - No Action - lights continue current sequence
- •Whole process repeats continuously to coordinate multiple traffic lights for safe traffic flow
6.1.5 Types of Sensors
| Sensor Type | What It Detects | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Heat/Cold levels | Central heating, air conditioning, refrigerators, weather stations |
| Pressure Sensor | Force/Pressure applied | Tire pressure monitoring, barometric pressure, industrial processes |
| Motion Sensor | Movement/Detects objects | Security alarms, automatic doors, gaming consoles |
| Light Sensor (LDR) | Light intensity | Street lighting, camera exposure, solar panels |
| Sound Sensor (Microphone) | Sound waves/Noise levels | Voice recognition, noise monitoring, security systems |
| Proximity Sensor | Nearby objects without contact | Parking sensors, touchless switches, mobile phones |
| Infrared (IR) Sensor | Infrared radiation/Heat signatures | Night vision, object detection, remote controls |
| Ultrasonic Sensor | Distance using sound waves | Parking assistance, robotics, level measurement |
| Humidity Sensor | Moisture/Water vapor in air | Greenhouses, HVAC systems, weather monitoring |
| Gas Sensor | Presence of specific gases | Carbon monoxide detectors, air quality monitoring |
| Accelerometer | Acceleration/Movement direction | Smartphones, gaming controllers, vehicle safety |
| Gyroscope | Orientation/Rotation | Drones, smartphones, navigation systems |
6.1.6 Comparison of Object Detection Sensors
| Sensor Type | How It Works | Range | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared (IR) | Emits IR light, detects reflection | Short (few cm to meters) | Low cost, works in dark, fast response | Affected by sunlight, limited range | Remote controls, proximity detection |
| LiDAR | Laser pulses measure distance | Long (up to 200m) | High accuracy, 3D mapping, works in various conditions | Expensive, complex, affected by fog/rain | Autonomous vehicles, mapping, robotics |
| Ultrasonic | Sound waves measure distance | Medium (few cm to 10m) | Works in dark, not affected by color, affordable | Affected by temperature, soft surfaces absorb sound | Parking sensors, robotics, level detection |
| Proximity | Detects nearby objects without contact | Very short (mm to cm) | No physical contact needed, reliable | Very limited range, can be affected by materials | Touchless switches, mobile phones, industrial automation |
6.1.7 Applications of Automated Systems
Industrial Applications
- •Manufacturing: Assembly lines, quality control, packaging
- •Process Control: Temperature, pressure, and flow regulation in chemical plants
- •Warehouse Management: Automated storage and retrieval systems
Transport Applications
- •Traffic Management: Automatic traffic lights, speed cameras
- •Parking Systems: Automated barriers, payment systems
- •Vehicle Systems: Cruise control, parking assistance, collision avoidance
Agriculture Applications
- •Irrigation Systems: Automatic watering based on soil moisture
- •Greenhouse Control: Temperature, humidity, and light regulation
- •Crop Monitoring: Drones with sensors for crop health assessment
Weather Monitoring
- •Weather Stations: Automatic collection of temperature, humidity, pressure, wind speed
- •Data Logging: Continuous monitoring and recording of weather data
Gaming Applications
- •Motion Controllers: Accelerometers and gyroscopes detect player movements
- •Virtual Reality: Sensors track head and hand movements
Lighting Applications
- •Smart Lighting: Automatic adjustment based on ambient light and occupancy
- •Energy Efficiency: Lights turn off when rooms are unoccupied
Scientific Applications
- •Laboratory Equipment: Automated experiments, data collection
- •Environmental Monitoring: Air quality, water quality sensors
6.2 Robotics
A robot is a machine capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically, especially one programmable by a computer. Robots combine sensors, actuators, and processing units to interact with their environment.
6.2.1 Characteristics of Robots
To be classified as a robot, it must have:
1. Ability to Sense Surroundings
- •Uses sensors (light, temperature, pressure, acoustic, etc.)
- •Sensors detect environment → send data to microprocessor/computer
- •Enables robots to recognise size, shape, weight, hot/cold conditions
2. Degree of Movement
- •Can move using wheels, cogs, pistons, gears
- •Perform actions: turning, lifting, gripping, twisting
- •Built from motors, actuators, hydraulic pipes, circuit boards
- •Use of end-effectors (attachments) for tasks like welding, spraying, cutting, lifting
3. Programmable
- •Have a controller (robot "brain") that decides actions
- •Controllers rely on sensor/camera input
- •Robots can be programmed for specific tasks
6.2.2 Uses of Robotics
Industry
Applications:
- • Assembly Lines: Welding, painting, assembling car parts
- • Material Handling: Moving heavy objects, palletizing
- • Quality Control: Inspection, testing products for defects
- • Packaging: Sorting, labeling, boxing products
Advantages
- ✓ Increased productivity
- ✓ Consistent quality
- ✓ Works 24/7
- ✓ Handles dangerous tasks
Disadvantages
- ✗ High initial cost
- ✗ Job displacement
- ✗ Requires maintenance
- ✗ Limited flexibility
Transport
Applications:
- • Autonomous Cars: Self-driving vehicles using sensors, AI, and GPS
- • Autonomous Trains: Driverless trains for public transport
- • Autonomous Airplanes (Drones): Unmanned aerial vehicles for delivery, surveillance
- • Warehouse Robots: Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for moving goods
Advantages
- ✓ Reduced accidents (human error)
- ✓ Improved traffic flow
- ✓ Fuel efficiency
- ✓ 24/7 operation
Disadvantages
- ✗ High development cost
- ✗ Security concerns (hacking)
- ✗ Job losses (drivers, pilots)
- ✗ Ethical dilemmas (decision-making)
Agriculture
Applications:
- • Harvesting Robots: Picking fruits and vegetables
- • Milking Robots: Automated milking systems for dairy farms
- • Weeding Robots: Identifying and removing weeds
- • Planting Robots: Automated seeding and planting
Advantages
- ✓ Addresses labor shortages
- ✓ Precise operations
- ✓ Works in all weather
- ✓ Increased yield
Disadvantages
- ✗ Expensive equipment
- ✗ Requires technical expertise
- ✗ May damage crops if malfunctioning
Medicine
Applications:
- • Surgical Robots: Assisting surgeons with precise operations (e.g., da Vinci system)
- • Rehabilitation Robots: Helping patients recover movement
- • Pharmacy Robots: Dispensing medications accurately
- • Prosthetics: Robotic limbs controlled by brain signals
Advantages
- ✓ Higher precision
- ✓ Minimally invasive surgery
- ✓ Faster recovery times
- ✓ Reduced human error
Disadvantages
- ✗ Very expensive
- ✗ Requires extensive training
- ✗ Technical failures can be critical
- ✗ Lack of human touch
Domestic
Applications:
- • Vacuum Robots: Automated floor cleaning (e.g., Roomba)
- • Lawn Mowing Robots: Automatic grass cutting
- • Window Cleaning Robots: Automated window washing
- • Security Robots: Patrolling and monitoring homes
Advantages
- ✓ Saves time
- ✓ Convenience
- ✓ Consistent cleaning
- ✓ Can work when owners are away
Disadvantages
- ✗ Limited capabilities
- ✗ Requires maintenance
- ✗ Can get stuck or lost
- ✗ Privacy concerns (security robots)
Entertainment
Applications:
- • Toy Robots: Interactive robots for children
- • Robotic Pets: Artificial pets that respond to interaction
- • Robotic Performers: Robots in theme parks, shows
- • Gaming Robots: Robots that play games with humans
Advantages
- ✓ Educational value
- ✓ Entertainment
- ✓ Can teach programming
Disadvantages
- ✗ Can be expensive
- ✗ Limited functionality
- ✗ May break easily
6.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and make decisions like humans. AI systems can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
6.3.1 Characteristics of AI
Mimics Human Intelligence
AI systems attempt to replicate human cognitive functions such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning.
Data Collection
AI systems gather and process large amounts of data to make informed decisions.
Rules
AI follows predefined rules or algorithms to process information and make decisions.
Reasoning
AI can analyze information, draw conclusions, and make logical decisions based on available data.
Learning
AI systems can improve their performance over time by learning from experience and data (machine learning).
Prediction
AI can forecast future outcomes based on patterns in historical data.
Pattern Recognition
AI can identify patterns, trends, and relationships in complex data sets that humans might miss.
6.3.2 Categories of AI
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
AI designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. Most current AI systems fall into this category.
Examples:
- • Voice assistants (Siri, Alexa)
- • Image recognition systems
- • Chess-playing programs
- • Recommendation systems (Netflix, Amazon)
General AI (Strong AI)
AI that possesses human-level intelligence and can perform any intellectual task that a human can do. This is still theoretical.
Note: General AI does not currently exist and remains a goal for future AI research.
6.3.3 Examples of AI
News Generation
AI systems can automatically generate news articles from data, financial reports, and sports statistics.
Smart Home Devices
AI-powered devices learn user preferences and automate home functions (lighting, heating, security).
Chatbots
AI programs that simulate conversation with users, providing customer support and answering queries.
Autonomous Cars
Self-driving vehicles use AI to navigate, detect obstacles, and make driving decisions.
Facial Recognition
AI systems that identify individuals from images or video, used in security, smartphones, and social media.
6.3.4 Expert Systems
An Expert System is a type of AI that mimics the decision-making ability of a human expert in a specific domain. It uses a knowledge base of facts and rules to solve problems and provide recommendations.
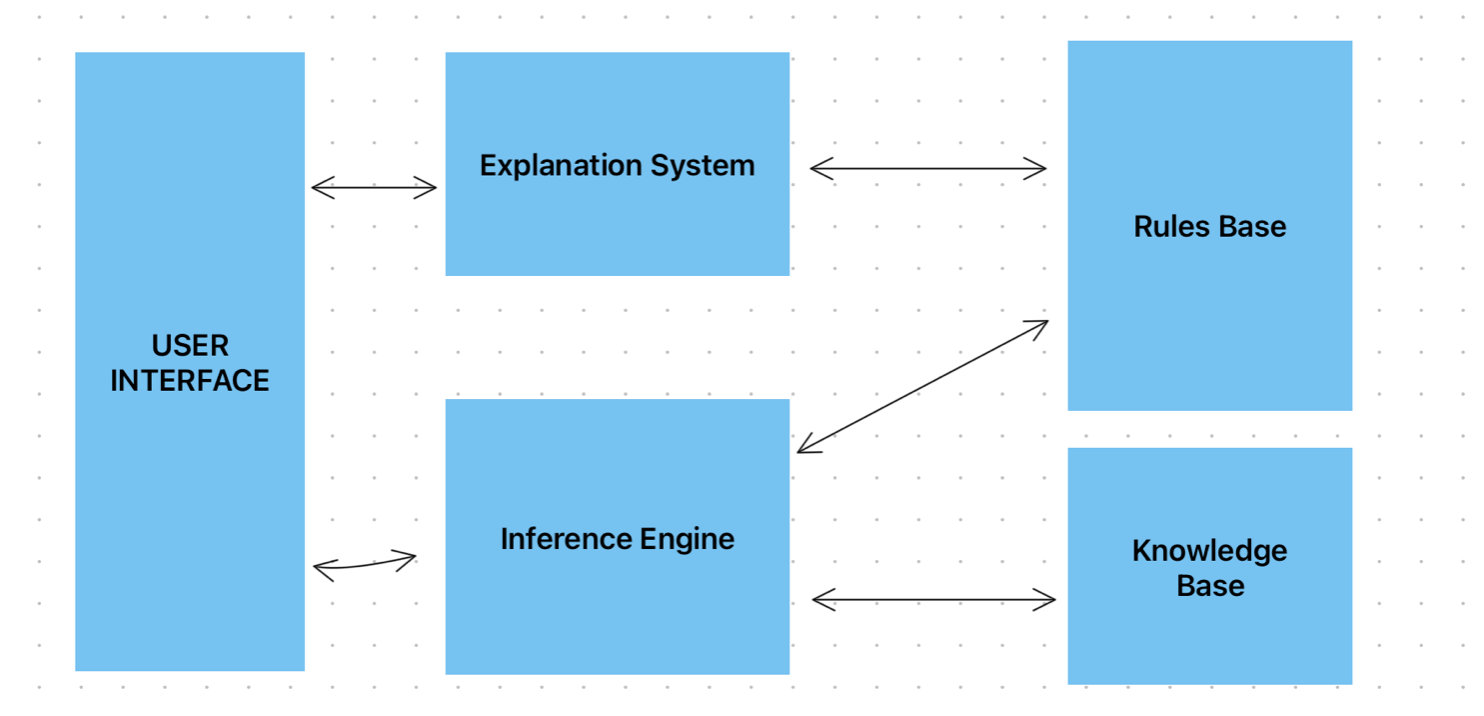
Components of an Expert System
Structure of Expert Systems
1. User Interface
Allows users to interact with the expert system, input questions, and receive answers or recommendations.
2. Inference Engine
The "brain" of the expert system. It processes user queries by:
- • Searching through the knowledge base
- • Applying rules to find solutions
- • Drawing conclusions based on available information
Exam Key Points:
- • The inference engine is used to decide which questions to ask the user.
- • This decision is based on the previous data input.
- • Symptoms input are located in/compared to the knowledge base.
- • It then applies the rule base to the knowledge base to decide the diagnosis.
3. Knowledge Base
Stores facts, information, and data about the specific domain. Contains:
- • Domain-specific knowledge
- • Historical data
- • Facts and information
4. Rules Base
Contains IF-THEN rules that define how to solve problems. Examples:
- • IF temperature > 38°C THEN patient has fever
- • IF engine temperature > 100°C THEN activate cooling system
5. Explanation System
Provides explanations for the expert system's conclusions, showing which rules and facts were used to reach a decision. This helps users understand and trust the system's recommendations.
Examples of Expert Systems
Example of Patient Diagnosis - Fever
The doctor enters the patient's symptoms in the system:
- • Fever (103°F)
- • Headache
- • Body Ache
- • Cough
Inference Engine
- • Compares the symptoms with medical facts in the Knowledge Base
- • Applies the rules in the Rules Base
Example Rule
If
- • Fever > 102.5°F
- • AND Cough = TRUE
- • AND Headache = TRUE
- • AND Body Ache = TRUE
Then
• Possible diagnosis: Flu (like influenza)
Knowledge Base
Stores factual medical data such as:
- • Typical temperature ranges for different illnesses
- • Associated symptoms for each illness
- • Seasonal outbreaks
Rules Base
- • IF Fever > 100°F AND Sore throat THEN seasonal infection
- • IF Fever > 103°F AND Rash THEN Measles
Explanation System
- • Explains the reasoning to the doctor
- • Suggests possible case of influenza based on very high temperature and body ache
Example of Geological Survey - Oil Exploration
User Interface
A geologist enters survey details into the system:
- • Seismic Survey Data
- • Magnetic Field Readings
- • Rock Sample Analysis
- • Location Coordinates
Inference Engine
- • Compares inputs with known geological patterns and facts stored in the Knowledge Base
- Example Rule:
If seismic readings show low-frequency reflections and rock density matches oil-bearing formations, then high probability of oil presence.
Knowledge Base
It is a repository of facts, a collection of objects and their attributes. Stores all the expert knowledge about a particular area obtained from many sources.
Example:
Stores comprehensive geological data, including:
- • Geological facts about rock types, structures, and formations
- • Seismic and magnetic profiles linked to oil, mineral, and other deposits
- • Characteristics of rocks known to contain oil or minerals
- • Historical drilling success in similar regions or formations
Rules Base
It is a collection of inference rules. These rules are used by inference engine to draw conclusions.
Example:
Logical rules based on IF and ELSE conditions, such as:
- • IF seismic data shows a dome structure AND high porosity rock, THEN possible oil reservoir
- • IF magnetic survey detects anomaly AND soil resistivity is low, THEN possible mineral deposit
- • IF characteristic rock type is present AND historical success in the region exists, THEN high probability of oil
Explanation System
Explains the reasoning behind its conclusions to the geologist:
- • Indicates a high probability of oil based on dome structure detected in seismic data, high porosity, and matching historical data from similar formations
- • Provides rationale for mineral deposit predictions when magnetic anomalies are supported by low soil resistivity readings
- • Justifies each output with reference to the stored knowledge and applied rules
6.3.5 Machine Learning
Machine Learning is where a computer system uses algorithms and statistical models to identify patterns in data and improve its performance at a task without being explicitly programmed.
- • Subset of AI: Machines learn from data without explicit re-programming
- • Algorithms trained on datasets → make predictions on new unseen data
- • Powerful for big data analysis & predictions
How Machine Learning Works
Training Data
Large amounts of data are fed to the ML algorithm
Pattern Recognition
Algorithm identifies patterns and relationships in the data
Model Creation
Algorithm creates a model based on learned patterns
Prediction/Decision
Model makes predictions or decisions on new, unseen data
Examples of Machine Learning
Spam Email Detection
Spam = Unwanted emails (ads, fraud, lottery, etc.). Ham = Normal/legitimate emails.
ML algorithms learn to identify spam emails by analyzing thousands of examples of spam and legitimate emails. The system improves over time as it processes more emails.
Features checked:
- • Words like "lottery, free, 100% guarantee" (spam indicators)
- • Sender reputation
- • Too many capital letters or links
The ML model then predicts if a new email is spam or ham.
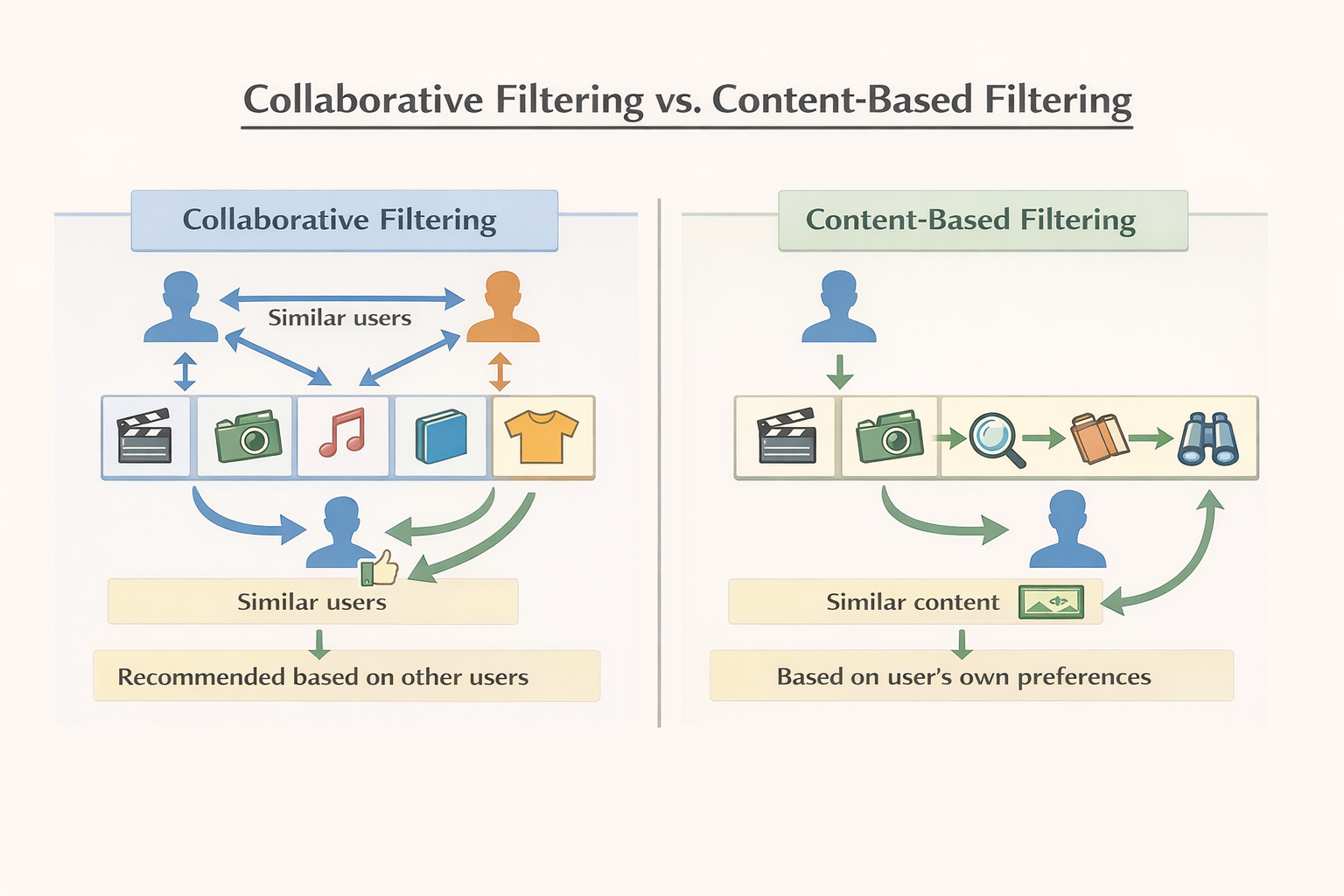
Recommendation Systems
ML algorithms analyze user behavior (what they watch, buy, like) to recommend similar content or products.
Example: Recommendation Systems (Spotify)
Spotify uses machine learning to recommend songs/playlists. It analyses attributes of songs such as:
- • Danceability → how suitable a track is for dancing
- • Energy → intensity, fast tempo
- • Speechiness → whether track is speech-heavy (like podcasts vs. songs)
- • Acousticness → whether it's acoustic or electronic
- • Valence → positivity/happiness of the song
- • Tempo → speed of the track
Based on these attributes, Spotify builds a profile of your music taste.
Two Approaches to Recommendations
1. Collaborative Filtering
"People like you also liked this."
- • Looks at user behaviour patterns
- • If Aarav and Priya both listen to Bollywood songs, and Priya also listens to Jazz, the system may recommend Jazz to Aarav too
- • Works even if you've never listened to Jazz before
2. Content-Based Filtering
"If you liked this, you'll like that."
- • Focuses on song attributes (e.g., if you like a fast, high-energy track → similar fast, high-energy songs are recommended)
- • Example: If Priya listens to "Dance Hits 2024," the system suggests other high-energy, high-danceability songs
👉 In real life, Spotify and Amazon use a hybrid (mix of both).
Fraud Detection
ML systems learn patterns of fraudulent transactions and can flag suspicious activities in real-time.
Practice Question
Past PaperExplain how the smart speaker can use machine learning to improve the voice command input.
Answer:
- •Gather data from the same/different voices // It can ask a user to say lots of different words
- •Analyse/identify patterns in a user’s voice
- •It can adapt its own processes
- •It can learn to identify a user’s voice
- •Stores successful/unsuccessful voice commands
- •It can learn different ways of making the same request
- •It can learn the different pronunciations // It can learn different accents
- •It can learn by listening to lots of different voices
- •It can learn to ignore any background/environmental noise if a user is speaking
Practice Question
Past PaperThe automated weather system is upgraded and given machine learning capabilities.
(i) Machine learning is part of a branch of computer science.
Identify the name of this branch of computer science. [1]
(ii) Explain how the machine learning capabilities can be used to predict future weather. [3]
Answer:
(i):
- •Artificial intelligence // AI
(ii) Any three from:
- •It can adapt its own processes/data.
- •It could analyse the data for trends/patterns.
- •... and predict future weather patterns based on the patterns.
- •Feedback is given on weather predictions.
- •... changes future predictions based on this feedback.
- •It could learn what weather occurs at certain times of year.
- •... and use this to predict what the weather would be like at the same time of year. ... and adapt its rules/processes for weather predictions.
Difference between AI and Machine Learning
| AI | Machine Learning |
|---|---|
| Simulates intelligence in machines | Subset of AI that learns from past data |
| Goal: Think like humans | Goal: Learn & improve from data |
| Rule-based + data-driven | Data-driven only |
| Broader field (reasoning, vision, speech, robotics) | Narrower, focused on learning patterns |
Extension: Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning → uses Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs).
Key Features:
- • Mimics the human brain with layers of neurons (input, hidden, output)
- • Handles complex tasks: face recognition, image processing, natural language understanding
- • Needs huge data + high computing power
- • Often described as a "black box" (hard to explain decision-making)
Examples of Deep Learning:
- • Image Recognition: Identifying objects in photos (used in self-driving cars, medical imaging)
- • Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding and generating human language (chatbots, translation)
- • Speech Recognition: Converting speech to text (voice assistants)
- • Face Recognition: Identifying individuals from images or video
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP = AI that understands and processes human language (text or speech).
Used in: chatbots, voice assistants (Alexa, Siri), Google Translate, spam filters.
Key Idea: Stop Words
Stop words = common words like the, is, and, of, in.
These are often removed in NLP because they don't add meaning.
Example:
Sentence: "The dog is running in the park"
After removing stop words → "dog running park"
This makes algorithms faster and focuses on the important parts.
6.3.6 Advantages and Disadvantages of AI
Advantages
- ✓Efficiency: Can process vast amounts of data quickly
- ✓Accuracy: Reduces human error in repetitive tasks
- ✓24/7 Operation: Works continuously without breaks
- ✓Decision Making: Can make objective decisions without emotions
- ✓Pattern Recognition: Identifies patterns humans might miss
- ✓Automation: Automates complex tasks, freeing humans for creative work
- ✓Medical Advances: Assists in diagnosis, drug discovery, treatment planning
Disadvantages
- ✗Job Displacement: Can replace human workers in various industries
- ✗High Cost: Development and maintenance can be expensive
- ✗Lack of Creativity: Cannot think creatively or outside programmed parameters
- ✗Ethical Concerns: Privacy, bias, decision-making accountability
- ✗Dependency: Over-reliance on AI systems can reduce human skills
- ✗Data Requirements: Requires large amounts of quality data to function well
- ✗Security Risks: Vulnerable to hacking and malicious use
- ✗Unemployment: Can lead to job losses in certain sectors